Understanding Adhesive Tape Allergy
What is Adhesive Tape Allergy?
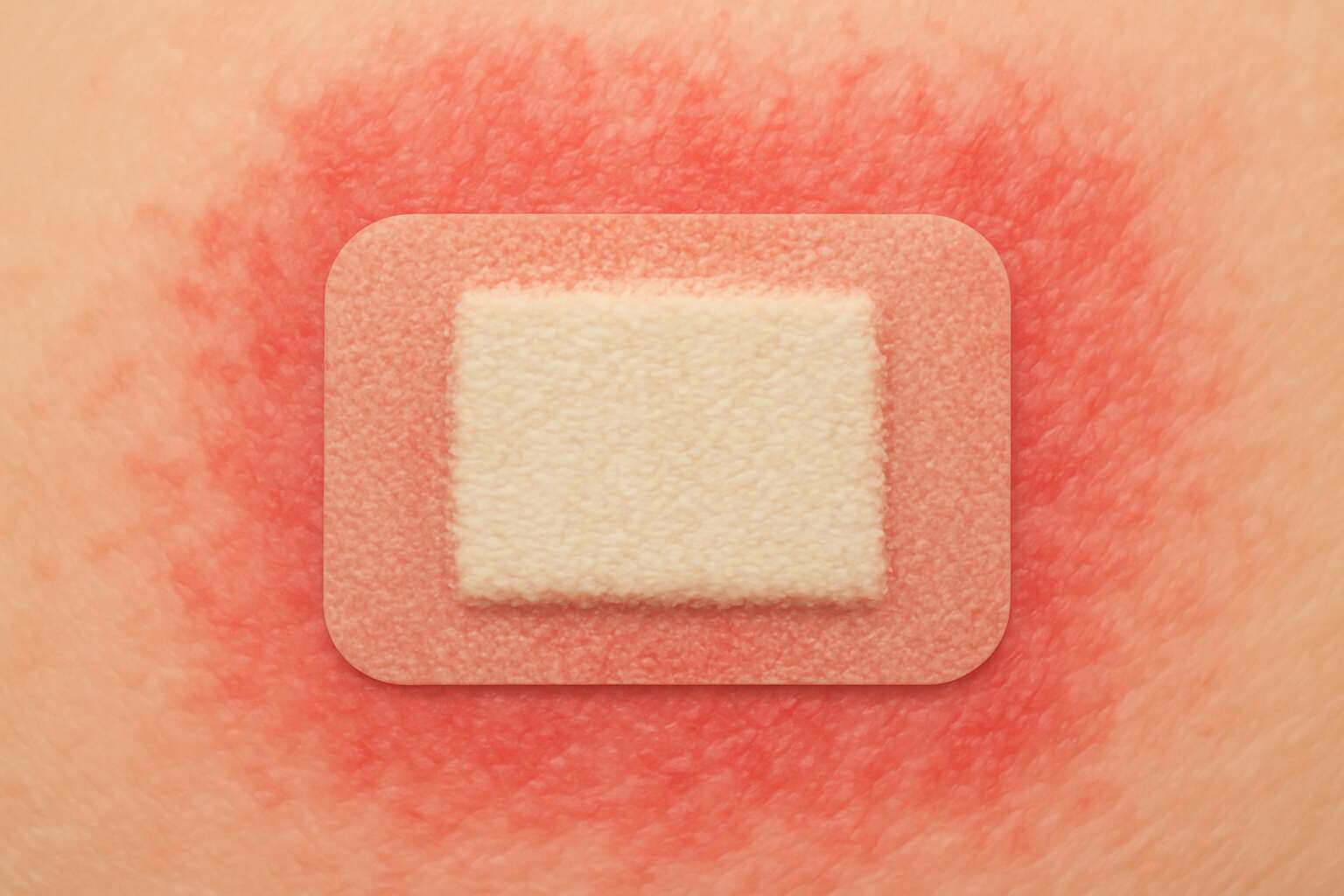
For many, the simple act of sticking a plaster or medical tape can lead to unexpected discomfort. Adhesive tape allergy is an often-overlooked condition that can cause irritation, redness, and even blistering. It’s a hidden adversary lurking behind everyday medical treatments and wound care routines. What makes this allergy particularly tricky is its subtle onset—initially mild, but capable of escalating into more severe skin reactions.
Understanding adhesive tape allergy is crucial, especially for those with sensitive skin or a history of allergies. This condition is classified under adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, a diagnostic code that helps healthcare professionals track and manage these reactions effectively. Allergic contact dermatitis from adhesive tapes manifests as an immune response to specific chemicals in the adhesive, such as latex or certain rubber compounds. Recognising these symptoms early can prevent prolonged suffering and complications.
To grasp the full scope of this allergy, it’s helpful to know the common triggers. These include:
- Latex-based adhesives
- Synthetic rubber components
- Chemical additives used in manufacturing
Common Symptoms and Signs
For those sensitive to adhesives, recognising the subtle signals of an allergic response can feel like deciphering a hidden language etched into the skin. The common symptoms and signs of adhesive tape allergy often manifest as an uninvited symphony of discomfort, whispering through redness and irritation. It’s not always immediate; sometimes, the first hint is a mild itch that gradually intensifies, like a secret unfolding beneath the surface.
Inflamed skin that becomes swollen, blistered, or crusted can be telltale signs of an immune reaction to the chemicals in the adhesive. Persistent itching, burning sensations, or a rash that refuses to fade are often the first clues. The skin may also develop small, fluid-filled blisters that cluster together—an unmistakable sign that the body is mounting a defence against an unwelcome intruder.
Understanding these symptoms is vital, especially for individuals with a history of allergies or sensitive skin. Recognising the early signs of adhesive tape allergy ensures swift intervention, reducing the risk of more severe skin reactions. When symptoms persist or worsen, consultation with a healthcare professional becomes essential, with the diagnosis often classified under adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 to streamline treatment and management.
Types of Allergic Reactions
In the shadowed corridors of dermatological afflictions, understanding the nature of allergic reactions to adhesive tapes reveals a tapestry woven with complexity. Not all reactions are created equal; some are fleeting whispers of irritation, while others are fierce, relentless storms that scar the skin. The spectrum of adhesive tape allergy is as varied as the shadows themselves, encompassing immediate hypersensitivity and delayed responses that lurk beneath the surface, ready to strike when least expected.
Immune responses to adhesive tapes can manifest as Type I or Type IV hypersensitivity reactions. Type I reactions, often rapid and intense, involve the release of histamines, leading to swelling and hives. Conversely, Type IV reactions are delayed, typically presenting as dermatitis weeks after exposure, with symptoms like redness, blistering, and crusting. Recognising these distinct types is crucial, especially when the diagnosis is categorised under adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, to ensure precise treatment.
To better comprehend the labyrinth of allergic responses, consider the following:
- Type I reactions are mediated by IgE antibodies, resulting in immediate symptoms such as swelling and itching.
- Type IV reactions involve T-cell mediated responses, often taking days to develop and causing eczema-like inflammation.
Understanding the types of allergic reactions is not merely academic; it is the key to unlocking effective management and fostering relief from the macabre grip of adhesive tape allergy.
Differentiating Allergic Contact Dermatitis from Irritant Contact Dermatitis
In the labyrinth of skin reactions, understanding the subtle distinctions between allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Though both can manifest as redness and discomfort, their origins diverge sharply. Allergic contact dermatitis, often linked to adhesive tape allergy, is driven by an immune response, typically involving Type IV hypersensitivity reactions. This delayed response can appear days after exposure, creating a perplexing puzzle for clinicians and patients alike.
In contrast, irritant contact dermatitis results from direct chemical or physical damage to the skin’s barrier, occurring almost immediately after contact with an irritant. The sensation can range from mild irritation to severe inflammation, but crucially, it does not involve immune system activation. Recognising these differences is essential, especially when considering the classification of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, which helps healthcare providers pinpoint the precise nature of the allergy and tailor treatments accordingly.
To clarify, consider these key points:
- Allergic contact dermatitis is immune-mediated, often developing after repeated exposure to adhesive components.
- Irritant contact dermatitis is a non-specific reaction caused by skin damage from adhesives or chemicals.
This differentiation not only influences diagnostic approaches but also directs appropriate management strategies, making the distinction between these dermatitis types more than mere semantics—it’s a matter of skin health and patient well-being. The shadows of uncertainty lift when the precise nature of the reaction is illuminated, especially within the realm of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 classifications.
Causes and Risk Factors of Adhesive Tape Allergy
Allergens in Adhesive Tapes
Adhesive tape allergy isn’t just a minor inconvenience; it’s a sneaky reaction that can turn a simple wound dressing into a skin battleground. Surprisingly, nearly 2% of the population is affected by adhesive tape allergy, highlighting just how common this problem really is. The culprits behind this allergic reaction are often found lurking in the adhesives themselves, which contain a cocktail of chemicals that can set off immune responses in sensitive individuals. These allergens typically include rubber compounds, acrylates, and other synthetic adhesives that, for some, act like an irritant magnet.
Risk factors for developing an adhesive tape allergy are as varied as the tapes themselves. Prolonged exposure is a notorious villain, especially in medical settings where dressings stay on longer than a Netflix binge. People with a history of eczema or other skin sensitivities are also more vulnerable, as their skin tends to be more reactive. Additionally, repeated exposure to adhesive tapes can lead to sensitisation, turning a once harmless adhesive into a potential allergen. For those with certain genetic predispositions, the odds of developing an adhesive tape allergy icd 10 classification are significantly higher, making awareness and early identification crucial for managing reactions effectively.
High-Risk Populations
Adhesive tape allergy isn’t just a minor irritation; it’s a complex immune response that can develop over time, especially in vulnerable populations. Certain causes and risk factors significantly elevate the likelihood of developing this condition, making awareness crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike. The primary culprits are the chemicals present in adhesives—rubber compounds, acrylates, and other synthetic substances—that can act as potent allergens. Continuous exposure to these substances, whether through medical dressings or everyday adhesives, increases the risk of sensitisation.
High-risk populations include individuals with a history of skin sensitivities such as eczema or contact dermatitis. Repeated exposure to adhesive tapes, especially in medical environments where dressings are often left on for extended periods, further compounds the risk. For some, genetic predispositions can mean a heightened susceptibility, leading to a diagnosis classified under adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 codes. Recognising these risk factors allows for better preventative strategies and early diagnosis, which are vital in managing allergic reactions effectively.
Environmental and Occupational Factors
Environmental and occupational factors play a pivotal role in the development of adhesive tape allergy, especially in individuals repeatedly exposed to adhesives in their daily routines or work environments. Prolonged contact with adhesives containing rubber compounds, acrylates, or other synthetic substances can act as potent allergens, triggering immune responses over time. In certain industries—such as healthcare, manufacturing, or construction—workers may encounter adhesive tapes daily, increasing their risk of sensitisation. Recognising these risks is vital, as these exposures can lead to chronic allergic reactions that significantly impact quality of life.
For some, genetic predispositions or pre-existing skin conditions, like eczema, further heighten susceptibility. The type of adhesive used, duration of contact, and environmental conditions—such as humidity and temperature—also influence the likelihood of an allergic response. In fact, the ICD 10 classification for adhesive tape allergy helps clinicians identify and document these complex cases, ensuring patients receive accurate diagnoses and tailored management. This nuanced understanding underscores the importance of awareness in preventing and addressing adhesive tape allergy.
Frequency of Exposure and Sensitization
For many individuals, repeated exposure to adhesives is an insidious process—sometimes occurring unnoticed until symptoms manifest quite unexpectedly. The frequency of exposure plays a pivotal role in the development of adhesive tape allergy, with some people experiencing sensitisation after just a few encounters, while others may require prolonged contact over months or years. This variability underscores the complex nature of allergic responses and why understanding the causes and risk factors is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
Those working in industries such as healthcare, construction, or manufacturing are particularly vulnerable due to their routine contact with adhesive tapes. For these individuals, the risk of developing an adhesive tape allergy increases with the duration and intensity of exposure. Factors like environmental conditions—especially humidity and temperature—also influence how the skin reacts to adhesives, making some environments more conducive to sensitisation.
Furthermore, genetic predispositions and pre-existing skin conditions such as eczema can significantly elevate susceptibility. Recognising these risk factors is crucial, as they often determine the likelihood of developing allergic contact dermatitis linked to adhesive tape allergy. When clinicians encounter such cases, they frequently consult the adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 classification to accurately document and understand the nuances of each patient’s condition, ensuring appropriate treatment pathways are initiated.
Diagnosing Adhesive Tape Allergy
Clinical Evaluation and Medical History
Diagnosing adhesive tape allergy requires a meticulous clinical evaluation combined with a comprehensive medical history. It’s fascinating how subtle skin changes can reveal so much about underlying sensitivities—often, patients present with persistent dermatitis that resists standard treatments. During the assessment, clinicians pay close attention to the pattern and timing of symptoms, as these clues can point towards an allergic response to adhesive components.
A detailed medical history is vital in identifying potential triggers and patterns of exposure. Patients are asked about their use of adhesive tapes in various settings, whether occupational or casual, and about any previous allergic reactions. To aid diagnosis, some practitioners utilise patch testing, which involves applying small amounts of common allergens, including those found in adhesive tapes, and observing reactions over several days. This approach helps differentiate adhesive tape allergy from other dermatological conditions and confirms the specific allergen responsible for the reaction.
Patch Testing and Other Diagnostic Methods
Unravelling the mystery of adhesive tape allergy can feel akin to deciphering an ancient script—each clue revealing a fragment of the story. Among the most illuminating diagnostic tools is patch testing, a procedure that acts as a portal into the hidden world of allergic sensitivities. During this process, small patches imbued with common allergens, including those found in adhesive tapes, are delicately placed on the patient’s skin.
Over the course of several days, clinicians observe for reactions—redness, swelling, or blistering—that signal an allergic response. This method is particularly valued for its ability to pinpoint adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, guiding practitioners towards precise diagnosis. Sometimes, patch testing is complemented by other diagnostic methods, such as:
- Serological tests to detect specific IgE antibodies
- Photopatch testing for UV-sensitive reactions
- Epicutaneous testing, which is a more extensive form of patch testing
Each approach weaves together to create a comprehensive picture—an essential step in differentiating adhesive tape allergy from other dermatological conditions. The magic lies in the detailed analysis, where pattern recognition and the timing of reactions often reveal the elusive allergen lurking beneath the surface.
Role of Dermatologists and Allergists
Diagnosing adhesive tape allergy is a delicate art, often requiring the keen eye of both dermatologists and allergists. These specialists possess an almost Sherlockian talent for piecing together the subtle clues that reveal an elusive allergy lurking beneath the surface. Their role extends beyond mere identification, encompassing a nuanced understanding of the patient’s history, exposure patterns, and the spectrum of potential allergens in adhesive tapes.
Central to this diagnostic journey is the meticulous process of patch testing, where allergens are applied to the skin to observe reactions. But it’s not a one-size-fits-all approach; sometimes, clinicians employ additional techniques such as serological tests for specific IgE antibodies or photopatch testing, especially when UV-sensitive reactions are suspected. These methods, woven together, form a comprehensive diagnostic tapestry, enabling precise identification of the adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 code.
In practice, clinicians often rely on a combination of detailed medical history and specialised testing to differentiate adhesive tape allergy from other dermatological conditions. This careful process ensures that the correct ICD 10 classification is assigned, guiding targeted management strategies. Ultimately, the role of these experts is to unravel the complex puzzle of allergic sensitivities, ensuring patients receive accurate diagnoses and appropriate care—an art that requires both scientific rigour and a touch of intuition.
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosing adhesive tape allergy can be as intricate as deciphering a cryptic manuscript. The differential diagnosis is essential to distinguish true allergy from other skin conditions that mimic its symptoms. Conditions such as irritant contact dermatitis, psoriasis, or even fungal infections can present with similar redness, itching, and discomfort.
Clinicians employ a thorough evaluation, integrating patient history with advanced diagnostic techniques. A detailed medical history often reveals exposure patterns, but it’s the specialised tests—like patch testing—that truly illuminate the culprit. Sometimes, clinicians may consider serological tests for specific IgE antibodies or photopatch testing, especially when photosensitive reactions are suspected.
- Patch testing with suspected allergens
- Serological testing for IgE antibodies
- Photopatch testing for UV-sensitive reactions
This multi-layered approach ensures an accurate diagnosis of the adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, guiding targeted treatment and avoiding unnecessary interventions. The goal is to untangle this complex web of skin sensitivities, revealing a clear pathway for effective management.
ICD-10 Coding for Adhesive Tape Allergy
Overview of ICD-10 Classification System
Understanding the intricacies of medical classification systems unveils a hidden order behind the chaos of human ailments. When it comes to adhesive tape allergy, the ICD-10 coding system plays a pivotal role in capturing the nuanced reality of allergic reactions. Recent statistics reveal that adhesive tape allergy icd 10 codes are increasingly utilised in clinical documentation, reflecting a growing awareness of this sensitive condition. The ICD-10 system, with its meticulous structure, assigns specific codes that encapsulate not just the allergy itself but also its severity and localisation. This meticulous approach enables healthcare professionals to track patterns, improve diagnosis accuracy, and refine treatment strategies.
Within the ICD-10 classification system, adhesive tape allergy falls under a broader spectrum of contact dermatitis codes, but there are precise codes dedicated to recognising allergic reactions caused by adhesive materials. These codes facilitate a detailed understanding of the patient’s condition, ensuring that each case is uniquely identified. For example, the ICD-10 code for allergic contact dermatitis due to adhesives is often distinguished from other dermatological conditions, highlighting the importance of accuracy in coding.
- Precise coding enhances epidemiological studies, revealing trends and risk factors.
- It supports insurance claims, ensuring proper reimbursement for allergy-related treatments.
- Clinicians can better communicate patient histories by referencing standardised ICD-10 codes.
Ultimately, the ICD-10 classification system for adhesive tape allergy icd 10 is more than a bureaucratic tool; it is a vital language that bridges the gap between clinical reality and medical record-keeping. Recognising its importance helps in understanding the broader impact of adhesive tape allergy on individual lives and the healthcare system at large.
Relevant ICD-10 Codes for Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Accurate ICD-10 coding for adhesive tape allergy is essential in capturing the true scope of allergic contact dermatitis caused by adhesives. Specific ICD-10 codes allow clinicians to differentiate between various types of dermatitis, providing clarity and precision in documentation. For adhesive tape allergy icd 10, the relevant codes typically fall under the section for allergic contact dermatitis, reflecting the immune-mediated nature of the condition.
These codes not only facilitate detailed medical records but also support epidemiological research and health data analysis. Recognising the importance of precise coding, clinicians often utilise the following codes for adhesive tape allergy:
- Chronic or recurrent allergic contact dermatitis due to adhesives – often coded as L23.3
- Unspecified allergic contact dermatitis, if the exact allergen or localisation isn’t determined – coded as L23.9
Accurately applying these ICD-10 codes ensures comprehensive documentation, ultimately improving patient management and enabling healthcare systems to track trends related to adhesive tape allergy icd 10 more effectively. This meticulous approach is vital, especially as awareness of adhesive-related allergies continues to rise in clinical practice.
How to Properly Document Adhesive Tape Allergy in Medical Records
Accurate ICD-10 coding plays a crucial role in properly documenting adhesive tape allergy cases within medical records. Proper documentation not only improves patient management but also enhances the visibility of adhesive tape allergy icd 10 trends across healthcare systems. When clinicians assign the correct codes, they help streamline data collection, making it easier to track epidemiological patterns and identify high-risk populations.
Typically, adhesive tape allergy is classified under the section for allergic contact dermatitis. The most relevant ICD-10 codes include L23.3 for chronic or recurrent allergic contact dermatitis caused by adhesives, and L23.9 for unspecified allergic contact dermatitis when localisation or allergen remains undetermined. Consistently applying these codes ensures that the allergic nature of the condition is clearly represented in medical records, supporting better patient care and research efforts.
To ensure comprehensive documentation, healthcare providers should consider the following steps:
- Review patient history meticulously to identify potential allergenic exposures.
- Apply the specific ICD-10 code that best fits the clinical presentation.
- Include detailed notes about the allergen suspected or confirmed, especially in complex cases.
In the context of adhesive tape allergy icd 10, precise coding is more than a bureaucratic necessity — it is a vital tool in understanding the true scope of this allergy within diverse populations. This meticulous approach facilitates better healthcare outcomes and supports ongoing research into allergen exposure and sensitisation patterns.
Importance of Accurate Coding for Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurate ICD-10 coding for adhesive tape allergy is more than a bureaucratic formality—it’s a cornerstone in advancing patient care and epidemiological understanding. Proper classification ensures that healthcare providers can effectively communicate the nature of allergic reactions caused by adhesives, leading to precise diagnosis and targeted treatment. When clinicians consistently assign the correct adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 codes, it becomes easier to track prevalence trends and identify high-risk populations, ultimately informing public health strategies.
Additionally, precise ICD-10 coding enhances data collection, enabling researchers and policymakers to monitor allergen exposure patterns over time. This level of detail supports the development of safer adhesive products and reinforces the importance of allergen avoidance in vulnerable groups. For healthcare providers, using the correct adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 codes like L23.3 or L23.9 ensures that the allergic contact dermatitis is properly documented, facilitating continuity of care and improving patient outcomes.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Immediate Relief and Symptom Control
When faced with the discomfort of adhesive tape allergy, swift and effective treatment is paramount. Immediate relief often involves gently removing the offending tape and cleansing the area with mild soap and water, reducing further exposure to allergens. Over-the-counter topical corticosteroids can soothe inflammation and alleviate itching, offering a welcome respite from persistent irritation.
Symptom control extends beyond initial steps. Anti-histamines may prove beneficial in dampening allergic responses, especially when itching becomes relentless. To prevent secondary infections, keeping the affected skin dry and avoiding scratching is essential. For persistent or severe reactions, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable. They might prescribe stronger topical or even systemic medications, tailored to the severity of the adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 diagnosis.
In some cases, a dermatologist may recommend an occlusive dressing or barrier creams to shield sensitive skin from further contact. Recognising that each patient’s reaction varies, a personalised approach ensures optimal management. Remember, a keen eye on environmental factors and the choice of hypoallergenic alternatives can make all the difference in conquering the irritation caused by adhesive tape allergy ICD 10.
Avoidance of Allergenic Adhesive Tapes
Effective treatment and management of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 require a strategic approach focused on avoiding exposure to known allergens. The cornerstone of this strategy is meticulous selection of hypoallergenic alternatives that minimise the risk of triggering a reaction. Patients are encouraged to scrutinise product labels carefully, opting for tapes free from common irritants and allergens. When purchasing new adhesive tapes, look for those marked as suitable for sensitive skin, which can significantly reduce the likelihood of an adverse response.
To optimise management, some practitioners recommend a systematic approach, often employing an ordered list to emphasise key steps:
- Identify and eliminate the allergenic tape from the environment.
- Use barrier creams containing zinc oxide or petrolatum to shield skin from potential allergens.
- Maintain skin integrity by keeping the area dry and clean, preventing secondary infections.
- Choose hypoallergenic adhesive tapes for any necessary future applications.
In addition, regular consultation with healthcare professionals ensures that individuals with adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 receive personalised advice tailored to their sensitivities. This careful avoidance not only alleviates current symptoms but also prevents future episodes, transforming a potentially debilitating allergy into a manageable condition. With each cautious choice, the path to comfort becomes clearer and more attainable.
Topical and Systemic Treatments
When battling the persistent discomfort of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, a multifaceted approach to treatment and management is essential. Topical remedies often serve as the first line of defence, with corticosteroid creams providing swift relief from inflammation and itching. These soothing applications can diminish symptoms while curbing secondary infections, especially when the skin barrier has been compromised.
For more stubborn cases, systemic treatments might be warranted. Oral antihistamines, for instance, can alleviate widespread allergic symptoms and facilitate comfort. In some scenarios, a short course of oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to quell severe reactions, always under professional supervision.
Practical management strategies include the use of barrier creams—zinc oxide or petrolatum—to shield sensitive skin from further exposure. An ordered list of key steps might look like this:
- Apply barrier creams before adhesive tape contact.
- Use hypoallergenic adhesive tapes designed for sensitive skin.
- Maintain skin integrity by keeping the area dry and clean.
- Consult healthcare professionals for personalised treatment plans.
In the realm of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, awareness and precision in treatment choices can turn a vexing allergy into a manageable condition, restoring skin health and peace of mind. The delicate dance of topical and systemic interventions underscores the importance of tailored care—an approach as nuanced as the social etiquettes we often navigate with finesse and subtlety.
Alternative Materials and Hypoallergenic Tapes
When confronting the stubborn shadows cast by adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, exploring alternative materials can be transformative. Hypoallergenic tapes, crafted with gentler adhesives and biocompatible substrates, offer a sanctuary for sensitive skin. These innovations are designed to minimise immune response, reducing the likelihood of allergic reactions.
For those seeking enhanced protection, the use of barrier creams such as zinc oxide or petrolatum creates an additional shield. These substances act as a formidable barrier, preventing allergens from penetrating and soothing irritated skin. Incorporating these practices can significantly diminish the severity of reactions associated with adhesive tape allergy ICD 10.
Additionally, selecting hypoallergenic tapes tailored for sensitive skin can make a profound difference. An ordered list of management strategies might include:
- Applying barrier creams prior to tape application to guard delicate skin.
- Opting for hypoallergenic or silicone-based adhesive tapes.
- Ensuring the skin remains dry, clean, and free from irritants.
- Consulting healthcare professionals for personalised treatment options tailored to individual sensitivities.
By embracing these innovative materials and meticulous skin care routines, individuals afflicted by adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 can navigate their daily routines with confidence. The quest for safe, hypoallergenic alternatives not only alleviates discomfort but also restores a sense of normalcy in a world often fraught with unseen allergens—turning a potential ordeal into a manageable chapter of health and resilience.
Prevention and Patient Education
Identifying and Avoiding Allergens
In the labyrinth of human skin, where resilience often masks underlying vulnerabilities, the spectre of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 lurks quietly yet insidiously. Prevention begins with a nuanced understanding of allergen exposure—a vital step in safeguarding those prone to hypersensitivity reactions. Educating patients about the importance of meticulous identification and avoidance of known allergens can significantly diminish the risk of developing adhesive tape allergy ICD 10. Knowledge is power; arming individuals with comprehensive insights into their specific sensitivities fosters proactive management and reduces reliance on reactive interventions.
One of the most effective strategies involves recognising environmental and occupational factors that may amplify susceptibility. For example, frequent exposure to certain adhesives in medical, industrial, or personal care settings can catalyse sensitisation. To assist in this, healthcare providers often recommend a systematic approach—such as maintaining detailed exposure logs—to track potential triggers. An awareness of high-risk populations, including those with pre-existing skin conditions, can further refine prevention efforts. When combined with patient education, this approach cultivates a vigilant mindset—crucial for avoiding the pitfalls of allergic contact dermatitis caused by adhesive tapes.
Reading Labels and Product Information
In the meticulous world of medical diagnostics, a simple label can make all the difference. When it comes to adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, reading labels and product information isn’t just a bureaucratic checkbox — it’s a crucial shield against unnecessary suffering. With many adhesive tapes containing hidden allergens, vigilance during procurement can prevent a cascade of dermatological grievances. Knowledge is power, and understanding the ingredients listed on packaging transforms patients from passive recipients of care into active participants in safeguarding their health.
Healthcare providers often emphasise the importance of scrutinising product details before application. An effective strategy involves maintaining a detailed log of products used, especially in environments with frequent exposure. This habit not only aids in pinpointing potential triggers but also streamlines future treatment plans. When selecting adhesive tapes, look for labels that specify hypoallergenic or latex-free options, reducing the risk of an adverse reaction.
- Check for known allergens such as latex or rubber compounds
- Review the list of adhesives and chemical constituents
- Prefer products with clear, comprehensive ingredient disclosures
Equally critical is understanding the ICD 10 codes associated with adhesive tape allergy. Proper documentation ensures precise diagnosis and effective treatment pathways. It also facilitates communication across healthcare teams and insurance providers. When patients are well-informed about the significance of accurate coding, they become partners in their health journey, minimising potential complications tied to misclassification. Ultimately, diligent reading of labels combined with meticulous documentation acts as a formidable defence against allergenic encounters, especially for those with a history of hypersensitivity reactions. Because in the realm of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, knowledge and vigilance are the most potent tools in the arsenal of prevention.
Workplace and Lifestyle Adjustments
Prevention of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 requires more than just awareness; it demands proactive adjustments in workplace and lifestyle choices. For individuals with heightened sensitivity, simple modifications can significantly reduce exposure to allergens and minimise the risk of severe reactions. Implementing workplace policies that promote the use of hypoallergenic or latex-free tapes can serve as a vital safeguard, especially in environments where frequent application is unavoidable.
Patients should be encouraged to educate themselves about the products they use daily. For example, selecting adhesive tapes with clear ingredient disclosures and avoiding those containing known allergens such as latex or rubber compounds is essential. Maintaining a detailed log of adhesive tape usage can help identify patterns that correlate with flare-ups, guiding future avoidance strategies.
Incorporating lifestyle adjustments, such as opting for alternative materials or specialised hypoallergenic tapes, can make a tangible difference. For those with a history of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, knowing how to navigate daily activities is crucial. Consider the following:
- Carefully read labels and product information before purchasing or applying adhesive tapes.
- Use barrier creams or protective coverings to minimise direct skin contact with potential allergens.
- Prioritise regular skin inspections to catch early signs of irritation or allergic reactions.
Workplace adjustments also play a pivotal role. Employers should facilitate access to hypoallergenic products and ensure protocols are in place for quick removal or replacement of problematic tapes. Such measures, combined with patient education, bolster the defence against adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 and help foster safer environments for all.
Patient Resources and Support Groups
In the journey towards managing adhesive tape allergy, patient education and access to reliable resources can be transformative. Awareness alone isn’t enough; empowering individuals with knowledge about allergen avoidance and symptom recognition is crucial. Support groups dedicated to adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 provide a vital lifeline, fostering community and shared understanding among those navigating this often-overlooked condition.
These groups offer a wealth of information, from practical tips for selecting hypoallergenic tapes to emotional support in facing daily challenges. Connecting with others who understand the intricacies of adhesive tape allergy ICD 10 can alleviate feelings of isolation and strengthen resilience. For many, realising they are not alone in their struggle is a beacon of hope.
Resources such as reputable websites, patient advocacy organisations, and educational pamphlets serve as invaluable tools. They guide patients through the labyrinth of product labelling, helping them decode ingredient disclosures and identify potential allergens. Engaging with healthcare providers who specialise in dermatology or allergy medicine further enhances a personalised approach to managing adhesive tape allergy ICD 10, ensuring that every step taken is rooted in expertise and compassion.

0 Comments